Rules and Regulations for Burial or Removal of Dead Bodies
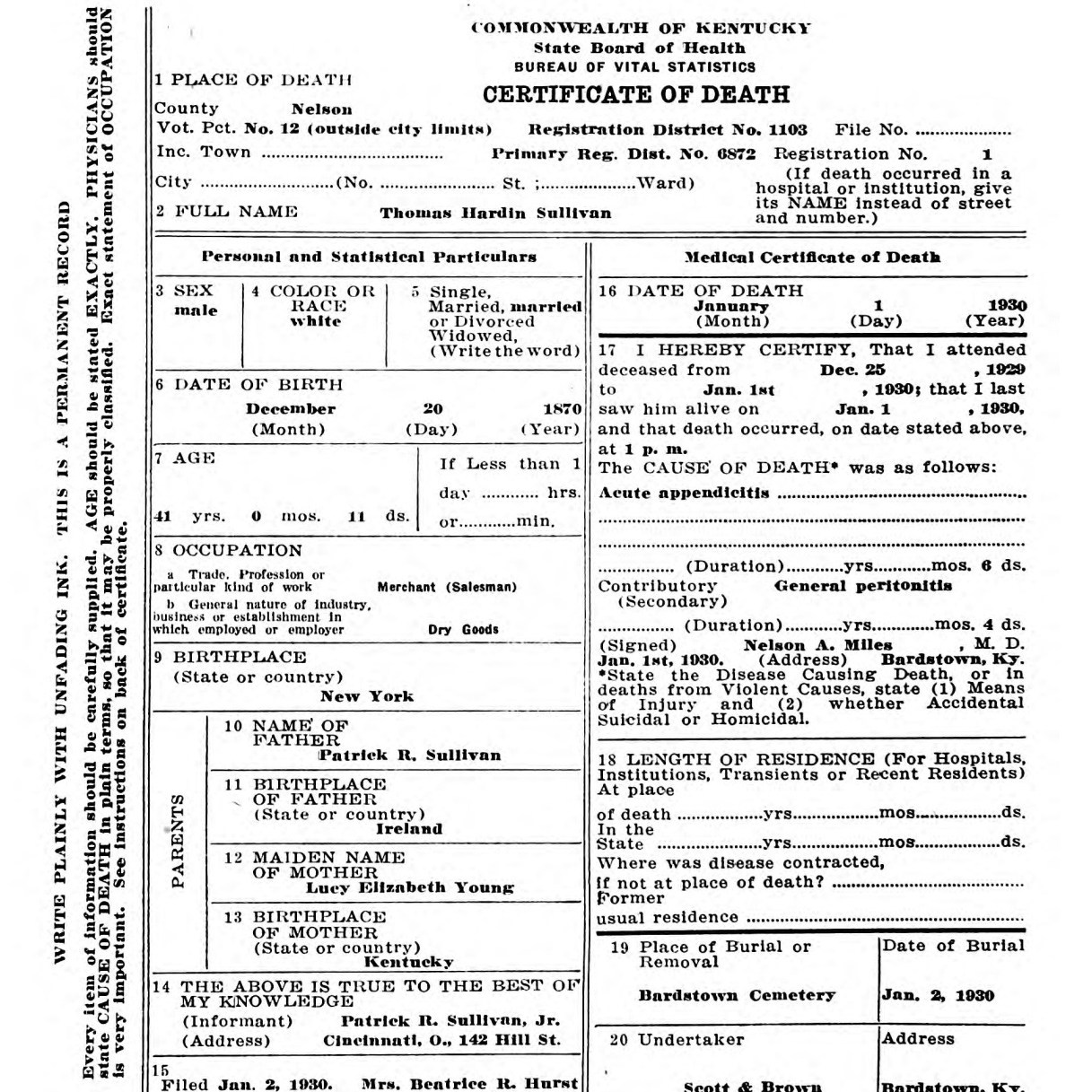
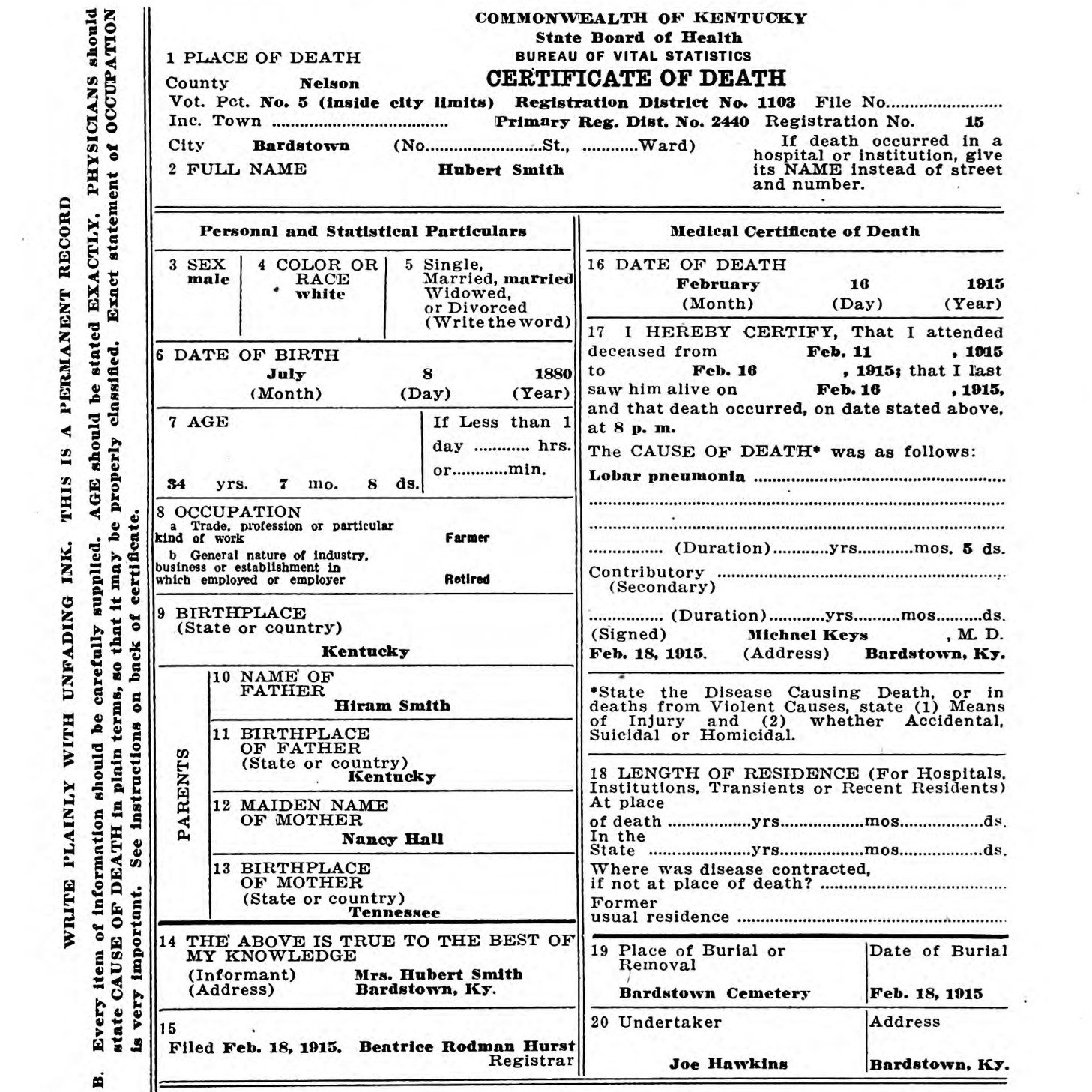
When a person dies in a local registrar’s district, it becomes the duty of the undertaker or person acting as such to procure a death certificate or a provisional death certificate if death occurs outside of the incorporated city or town; he secures the information asked for on the left side of the certificate from anyone having a knowledge of the facts, and secures the informant’s signature. He then presents the certificate to the doctor in charge or last in attendance, who gives the items that appear on the right side of the certificate of death over his signature. The person acting as undertaker then presents the completed certificate of death to the local registrar of the district in which the death occurred, or to a deputy registrar or sub-registrar; the local registrar then issues a burial or removal permit which constitutes the authority for the burial. The undertaker gives this to the sexton in charge of the burying ground, and the sexton returns the burial or removal permit to the local registrar of this district, who keeps it in his office for one year.
When a death occurs outside of the limits of a town or city, the undertaker, or person acting as such, can go to the nearest local registrar and file a “provisional death certificate,” which is a promise under law to secure the complete death certificate with five (5) days and deliver it to the local registrar of the district where the death occurred. When the undertaker, or person acting as such, signs such a provisional death certificate, the local registrar who keeps this issues him a burial or removal permit and the funeral can take place as provide by law. Should the undertaker fail to secure this complete death certificate within five days, he is subject to a fine and the possibility of having his license revoked.


Rule 48 – Duties of Undertakers – Section 2049
It shall be the duty of every undertaker taking charge of the preparation for the burial of the body of any person to ascertain whether such person died of a communicable disease and if such person died of Asiatic cholera, diphtheria, epidemic cerebrospinal meningitis, glanders, plague, scarlet fever, smallpox or typhus fever, it shall be his duty to cause it immediately to be wrapped in a sheet saturated with disinfecting solution and promptly thereafter placed in a coffin or casket, which shall then be immediately and permanently closed. This regulation shall not be construed to prohibit the embalming of any such body, but the undertaker shall cause such embalming to be done immediately upon taking charge of the body, except that, when a permit for embalming is required, this shall not proceed until the receipt of such permit. But immediately after the embalming he shall cause such body to be wrapped in a sheet and placed in a coffin or casket as hereinabove directed.
After handling, embalming or preparing for burial the body of a person dead of any of the communicable diseases enumerated in this rule, such parts of the person’s garments, and utensils or other articles of the undertaker or his assistants, as may have been liable to contamination with infective material, shall be immediately cleansed or disinfected or sterilized according to the requirements of the local Board of Health
Rule 40 – Public Funerals Forbidden in Certain Cases – Section 2049
A public church funeral shall not be held of any person who has died of diphtheria, measles, scarlet fever, smallpox, typhus fever or poliomyelitis, unless the body is enclosed in a properly sealed casket, and the consent of the local Health Officer has first been obtained.
Rule 171 – Burial and Removal of Dead Bodies – Section 2049
No dead body shall be disinterred between May 1st and October 1st of any year unless such body has been buried five years or longer. No dead body shall be disinterred or removed at any time except upon a special permit issued by the State Registrar upon application filed by the party desiring to make such disinterment and removal. Provided: Local registrars may issue permits for disinterment of bodies to be removed from one grave to another in the same cemetery in their own district if death did not result from any of the diseases mentioned in Rule 48.
Rule 172 – Preparation of Disinterred Bodies
Every disinterred body, dead from any disease or cause, shall be treated as infectious or dangerous to the public health and shall not be removed or accepted for transportation until said remains or coffin or casket containing same has been wrapped in a sheet thoroughly saturated with an approved disinfectant fluid and inclosed [sic] in a hermetically sealed metal or metal lined box. The foregoing requirement may be waived at the discretion of the State Registrar if it is shown in the permit that the body to be disinterred was embalmed and originally buried in a hermetically sealed or otherwise air-tight metal casket, box or vault. Bodies properly embalmed and deposited in receiving vaults will not be considered as buried, but may be removed for transportation and burial any time within thirty days from date of death without a special permit required in Rule 171. After thirty days from date of death all such bodies shall be considered and treated as buried bodies.
Rule 173 – Sale of Coffins
No person, firm or corporation shall sell or furnish any coffin or casket for the burial or disposition of dead bodies until the purchaser shall have filed with the local registrar a complete death certificate and secured a burial permit. Provided, this rule shall not apply to persons, firms or corporations engaged in the wholesale manufacture or selling of coffins or caskets.

Transportation of Dead
Rule 174 – Transit Permit and Label Necessary – Section 2049
A transit permit and transit label issued by the proper health authorities shall be required for each dead body transported by common carrier. The transit permit shall state the name, sex, color and age of the deceased, the cause and date of death, the initial and terminal points, a statement as to the method of preparation of the body, the date of issuance, the signature of the undertaker, the signature and the title of the officer issuing the permit. The transit label shall state the place and date of death, the name of the deceased, the name of the escort consignee, the initial and terminal points, the date of issuance, the signature and official title of the officer issuing the permit, and shall be attached to the outside case.
Rule 175 – Transportation of Bodies Dead from Communicable Disease
The transportation of bodies dead of smallpox, plague, Asiatic cholera, typhus fever, diphtheria (membrane croup, diphtheritic sore throat), erysipelas, anthrax and leprosy, shall be permitted only under the following conditions:
- The body shall be thoroughly embalmed with an approved disinfectant fluid
- All orifices shall be closed with absorbent cotton
- The body shall be washed with disinfectant fluid, enveloped in a sheet saturated with the same, and placed at once in a coffin or casket, which shall be immediately closed
- The coffin or casket or the outside case containing the same shall be metal, or metal-lined, and hermetically and permanently sealed
Rule 176 – Transportation of Bodies Dead of Any Disease Other Than Communicable Disease
- (a) The transportation of bodies dead of any disease other than those mentioned in Rule 175 shall be permitted under the following conditions:
- (b) When the destination can be reached within twenty-four hours after death, the coffin or casket shall be encased in a strong outer box made of good sound lumber not less than seven-eighths of an inch thick; all joints must be tongued and grooved; top and bottom put on with cleats or crosspieces
When the destination cannot be reached within twenty-four hours after death, the body shall be thoroughly embalmed and the coffin or casket placed in an outside case constructed in Paragraph (a).
Rule 177 – Transportation of Any Disinterred Body
No disinterred body dead from any disease or cause shall be transported by common carrier unless approved by the health authorities having jurisdiction at the place of disinterment, and transit permit and transit label shall be required as provided in Rule 174. The disinterment and transportation of bodies dead of diseases mentioned in Rule 175 shall not be allowed except by special permission of the health authorities at both the place of disinterment, and the point of destination. All disinterred remains shall be prepared in accordance with Rule 175; Provided, that bodies in a receiving vault when prepared by licensed embalmers shall not be regarded as disinterred bodies until after the expiration of thirty days.
Rule 178 – Outside Case May be Omitted
The outside case may be omitted in all instances when the coffin or casket is transported in hearse or undertaker’s wagon.
Rule 179 – Specifications for Outside Case
Every outside case shall bear at least four handles, and when over 5 feet six inches in length, shall bear six handles.
Rule 180 – Approved Disinfectant Fluid
An approved disinfectant fluid shall contain not less than 5 per cent of formaldehyde gas, or its equivalent; the term “embalming,” as employed in these rules, shall require the injection by licensed embalmers of not less than 10 per cent of the body weight, injected arterially in addition to cavity injection; and twelve hours shall elapse between the time of embalming and the shipment of the body.
Contributed by Shawn Logan | contact@kyhi.org
⁘ Works Cited ⁘
- Bulletin of the State Board of Health of Kentucky, Vol. VII, No. 2, Sept., 1934
Important note:
If you would like to use any information on this website (including text, bios, photos and any other information) we encourage you to contact us. We do not own all of the materials on this website/blog. Many of these materials are courtesy of other sources and the original copyright holders retain all applicable rights under the law. Please remember that information contained on this site, authored/owned by KHI, is provided under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Photographs, text, illustrations and all other media not authored by KHI belong to their respective authors/owners/copyright holders and are used here for educational purposes only under Title 17 U.S. Code § 107.
